What are the applications of NTC negative temperature coefficient thermistors?
Three conventional applications for thermistors: surge absorption, temperature measurement, and temperature compensation. NTC Thermistor It is a negative temperature coefficient thermistor. The resistance decreases with the increase of temperature. The material used is a semiconductor material with a large negative temperature coefficient. This resistor is widely used in switching power supplies, UPS power supplies, electronic ballasts, temperature sensors, and automatic adjustment heaters.
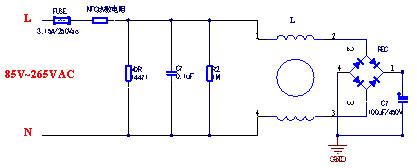
1. Suppress inrush current
This type of thermistor is of a power type, although the volume is small, but the power is large. Typically connected in series on the input line, it has a nominal zero power resistance value. Generally, this resistance is very small, and the zero-power resistance is the most basic parameter of the thermal resistor. This parameter is generally given by the manufacturer. When connected in series in the power supply loop, the starting surge current can be effectively suppressed, and the power it consumes is almost negligible.
Power type thermistor features:
1 small size, high power
2 strong ability to suppress surge current, fast response
3 material constant (B value) is large
4 long life, high reliability, wide working range
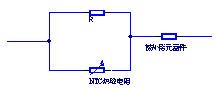
Power type thermistor specific line connection
2, for temperature sensor temperature measurement
As a thermistor for measuring temperature, it utilizes the change of external temperature resistance. Because the NTC resistor always passes a certain amount of current when it is connected to the circuit, this current will cause the NTC to generate heat itself, and the NTC resistance will decrease, which will have a great impact on the measurement. Therefore, it is necessary to control the self-heating to prevent the current flowing through the thermistor from being too large, causing the component itself to generate heat and causing measurement errors. Write all or part of the resistance value corresponding to the temperature into the CPU, so that the resistance value changes when the external temperature changes, and the voltage changes. This package has a patch type, epoxy head type, glass seal type, straw hat type, etc.
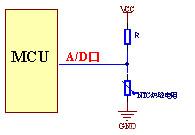
Thermistor temperature measurement line example diagram
Using the principle of resistor divider, the voltage changes when the NTC resistor value changes. Use the A/D port to detect the change in voltage, and write all the data to be used in the thermistor into the MCU. Different resistance values correspond to different temperatures, and the program is continuously tested.
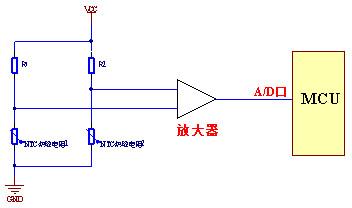 If the temperature accuracy is required to be higher, high-precision NTC can be used, and a bridge circuit plus amplifier can be used. The thermistor NT1/NT2 and the resistors R1 and R2 form a bridge circuit. As long as the thermistor has a temperature difference, the amplifier outputs a corresponding signal.
If the temperature accuracy is required to be higher, high-precision NTC can be used, and a bridge circuit plus amplifier can be used. The thermistor NT1/NT2 and the resistors R1 and R2 form a bridge circuit. As long as the thermistor has a temperature difference, the amplifier outputs a corresponding signal.
3, temperature compensation
In some electrical appliances, the accuracy is very high, especially in instrumentation, where many components are made of wire. For example, wirewound resistors, metals generally have a positive temperature coefficient and can be compensated with a negative temperature coefficient thermistor. One positive and one negative can offset the error caused by temperature changes and improve accuracy. As a temperature compensation, the alloy copper wire resistance is generally connected in parallel with the NTC thermistor and then connected in series with the compensated component.

1. Suppress inrush current
This type of thermistor is of a power type, although the volume is small, but the power is large. Typically connected in series on the input line, it has a nominal zero power resistance value. Generally, this resistance is very small, and the zero-power resistance is the most basic parameter of the thermal resistor. This parameter is generally given by the manufacturer. When connected in series in the power supply loop, the starting surge current can be effectively suppressed, and the power it consumes is almost negligible.
Power type thermistor features:
1 small size, high power
2 strong ability to suppress surge current, fast response
3 material constant (B value) is large
4 long life, high reliability, wide working range
Power type thermistor specific line connection

2, for temperature sensor temperature measurement
As a thermistor for measuring temperature, it utilizes the change of external temperature resistance. Because the NTC resistor always passes a certain amount of current when it is connected to the circuit, this current will cause the NTC to generate heat itself, and the NTC resistance will decrease, which will have a great impact on the measurement. Therefore, it is necessary to control the self-heating to prevent the current flowing through the thermistor from being too large, causing the component itself to generate heat and causing measurement errors. Write all or part of the resistance value corresponding to the temperature into the CPU, so that the resistance value changes when the external temperature changes, and the voltage changes. This package has a patch type, epoxy head type, glass seal type, straw hat type, etc.

Thermistor temperature measurement line example diagram
Using the principle of resistor divider, the voltage changes when the NTC resistor value changes. Use the A/D port to detect the change in voltage, and write all the data to be used in the thermistor into the MCU. Different resistance values correspond to different temperatures, and the program is continuously tested.

3, temperature compensation
In some electrical appliances, the accuracy is very high, especially in instrumentation, where many components are made of wire. For example, wirewound resistors, metals generally have a positive temperature coefficient and can be compensated with a negative temperature coefficient thermistor. One positive and one negative can offset the error caused by temperature changes and improve accuracy. As a temperature compensation, the alloy copper wire resistance is generally connected in parallel with the NTC thermistor and then connected in series with the compensated component.







