Sensing circuit design solution for simulating temperature sensor temperature
Unlike thermistors, TI analog temperature sensors measure very well over a wide temperature range and have a linear output over the entire operating range. You don't have to worry about the inventory of different devices. In addition, TI's unique design also makes these devices extremely low current and low noise sensitivity. Shown in Figure 1 is the output of the TI LMT84 low-cost analog temperature sensor, whose output remains linear from -50oC to 150oC.
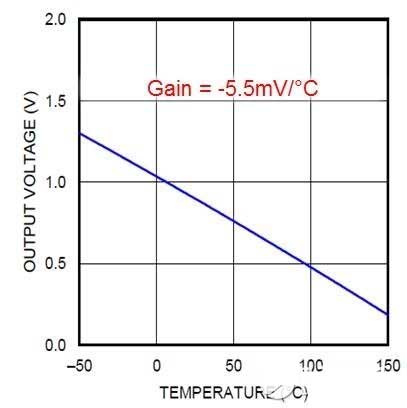
Figure 1: Relationship between LMT84 output voltage and temperature
Figure 2 shows a typical application of one of the TI LMT series analog temperature sensors, in which only IC is used and no external components are used.
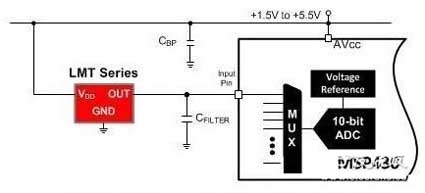
Figure 3 shows a comparison of the current consumption curve of the same device versus the current consumption curve of a typical thermistor. The LMT84 consumes 5μA (in the temperature range of -50oC to 150oC), while the thermistor consumes between 101μA and 315μA.
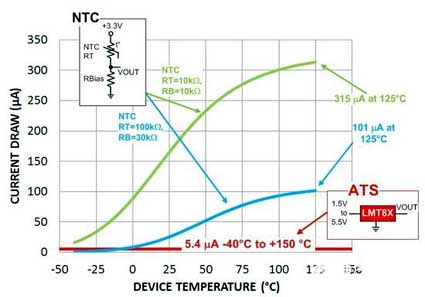
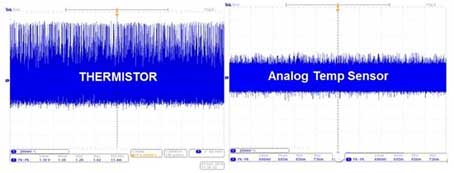
Figure 4: Noise experiment with thermistor and analog temperature sensor connected to the switching regulator

Figure 1: Relationship between LMT84 output voltage and temperature
Figure 2 shows a typical application of one of the TI LMT series analog temperature sensors, in which only IC is used and no external components are used.

image 2: Analog Temperature Sensor Solution (LMT Series)
Figure 3 shows a comparison of the current consumption curve of the same device versus the current consumption curve of a typical thermistor. The LMT84 consumes 5μA (in the temperature range of -50oC to 150oC), while the thermistor consumes between 101μA and 315μA.

Figure 3: Power dissipation—a comparison between thermistor and analog temperature sensing
Figure 4 shows a comparison of the operating noise of an analog temperature sensor mounted on a switching regulator and a thermistor in a noisy environment. At room temperature, the thermistor and the sensor have the same noise level, but in a higher temperature environment, the noise level becomes worse due to the lower resolution of the thermistor. Typically, the analog temperature sensor's operating noise is three times lower than the thermistor's noise level.

Figure 4: Noise experiment with thermistor and analog temperature sensor connected to the switching regulator
For a very narrow temperature range (typically between 0oC and 70oC), the thermistor works well due to its narrow range, high linear range and cost effectiveness. Although specially calibrated thermistors can be used to achieve target accuracy for specific temperatures, their cost is too high and maintaining inventory of these different devices is also difficult. Analog temperature sensors eliminate these challenges and are competitive in terms of cost. Please leave a message below, share with me your experience with these devices, and how you can solve the system temperature sensing problem. For information on TI's temperature sensor portfolio and other applications, please visit the links listed in other resources.





