2018 Encapsulation over-current self-recovery fuse
- PRODUCT DETAIL
The operating principle of the resettable fuse is a dynamic balance of energy. The current flowing through the resettable fuse generates a certain amount of heat due to the thermal effect of the current (all resettable fuses have a resistance value). The heat generated is totally or partially dissipated to the environment, and the heat that is not dissipated will raise the temperature of the resettable fuse element. The temperature during normal operation is relatively low, and the heat generated and heat radiated is in equilibrium. The resettable fuse element is in a low resistance state, and the resettable fuse does not operate. When the current flowing through the resettable fuse element increases or the ambient temperature increases, if the balance between the generated heat and the radiated heat is reached, the resettable fuse still does not operate. When the current or ambient temperature is increased, the resettable fuse will reach a higher temperature.
If the current or ambient temperature continues to increase at this time, the heat generated will be greater than the heat emitted, which will cause the temperature of the resettable fuse element to increase sharply. At this stage, a small temperature change will cause a large increase in resistance value. At this time, the resettable fuse element is in a high resistance protection state. The increase in impedance limits the current, which drops sharply in a short period of time, thereby protecting the circuit equipment from damage. As long as the heat generated by the applied voltage is sufficient to dissipate heat from the resettable fuse element, the resettable fuse element in a changed state can always be in an operating state (high resistance).
When the applied voltage disappears, the resettable fuse can automatically recover.
If the current or ambient temperature continues to increase at this time, the heat generated will be greater than the heat emitted, which will cause the temperature of the resettable fuse element to increase sharply. At this stage, a small temperature change will cause a large increase in resistance value. At this time, the resettable fuse element is in a high resistance protection state. The increase in impedance limits the current, which drops sharply in a short period of time, thereby protecting the circuit equipment from damage. As long as the heat generated by the applied voltage is sufficient to dissipate heat from the resettable fuse element, the resettable fuse element in a changed state can always be in an operating state (high resistance).
When the applied voltage disappears, the resettable fuse can automatically recover.
Area of application: all high-density circuit boards
Features: surface mount components, SMD fuse moves faster than normal
Working current: 0.3A ~ 2A
Operating temperature range: -40 ℃ to 85 ℃
Lead-free, halogen-free, environmentally friendly products, RoHS and REACH standards
Features: surface mount components, SMD fuse moves faster than normal
Working current: 0.3A ~ 2A
Operating temperature range: -40 ℃ to 85 ℃
Lead-free, halogen-free, environmentally friendly products, RoHS and REACH standards


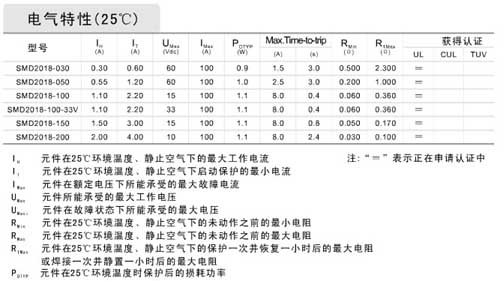
| Sign | Definition |
| Ih | Hold current-maximum current at which the device will not trip at 25℃ |
| It | Trip current-minimum current at which the device will always trip at 25℃ |
| Vmax | Maximum voltage at which the device will not trip |
| Vmaxi | Maximum voltage device can withstand without damage at it rated current |
| Imax | Maximum fault current device can withstand without damage at rated voltage |
| Rmin | Minimum device resistance at 25℃ prior to tripping |
| Rmax | Maximum device resistance at 25℃ prior to tripping |
| Figure | The Figure of PTC |
| Lead | Lead diameter |











