0603 SMD Resettable Fuses for battery pack
- PRODUCT DETAIL
Resettable fuses for battery protection
a, Cell phone battery pack:
The key to the cell phone battery pack is its application characteristics. This battery is housed in a small, light and narrow box.
NICD, NiMH, Li-ION, these three main chemical batteries are all housed in this kind of universal box.
Generally, the working voltage of the battery pack is less than 10V, and the maximum charging voltage is 16V. The operating voltage of the latest battery packs is even lower, between 3 and 4V.
This means that the packaging of the battery pack changes very quickly, from soldered ribbons to placement components on printed circuit boards.
Battery packs need circuit protection devices, such as VTP210G, which can keep the current at about 1 amp at 60C.
The lower the resistance value of the protection circuit, the smaller the energy loss, and the larger the space for component selection.
b. Cordless phone battery: The current and voltage passed by the cordless phone is relatively small. SRP120, LTP070 and LTP100 are all good overcurrent protection components.
c. Radio communication battery: Radio communication uses more current than cell phone batteries and less current than laptop computers. The LR4 series has a working current of 7.3 amps, is small in size and light in weight, and is very suitable for this application. SRP or LTP series with large operating current is also applicable.
1.Application of resettable fuse in rechargeable battery pack
1) Problems and analysis: NICD, NiMH, Li-ION are often used in special protection circuits for mobile phones and computers.
The causes of these battery pack failures are usually: The positive and negative terminals are accidentally shorted; the charger cannot stop charging a fully charged battery; Reverse the polarity of the charger or battery. The PTC chip series is installed in series in each unit of the battery pack to provide overcurrent and overtemperature protection to the circuit.
2) Protection requirements: When a fault occurs, the voltage of the mobile phone can reach 16V, and the voltage of the computer can reach 24V; Its current can reach 100 amps. Under overcharge conditions, the battery pack needs to be protected from over-temperature. NiCD batteries cannot exceed 120C, and NiMH and Li-ION batteries cannot exceed 90C.
Applications: All high-density circuit boards
Features: Surface mount components, faster than ordinary SMD fuse action
Working current: 0.1A ~ 1.0A
Operating temperature range: -40 ℃ to 85 ℃
Lead-free, halogen-free environmentally friendly products, RoHS and REACH standards
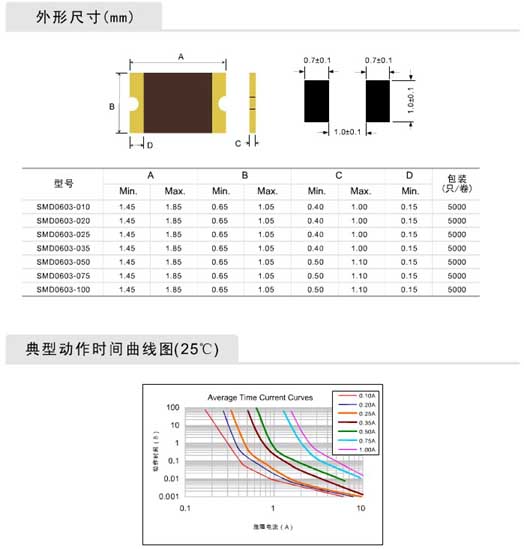
Model
a, Cell phone battery pack:
The key to the cell phone battery pack is its application characteristics. This battery is housed in a small, light and narrow box.
NICD, NiMH, Li-ION, these three main chemical batteries are all housed in this kind of universal box.
Generally, the working voltage of the battery pack is less than 10V, and the maximum charging voltage is 16V. The operating voltage of the latest battery packs is even lower, between 3 and 4V.
This means that the packaging of the battery pack changes very quickly, from soldered ribbons to placement components on printed circuit boards.
Battery packs need circuit protection devices, such as VTP210G, which can keep the current at about 1 amp at 60C.
The lower the resistance value of the protection circuit, the smaller the energy loss, and the larger the space for component selection.
b. Cordless phone battery: The current and voltage passed by the cordless phone is relatively small. SRP120, LTP070 and LTP100 are all good overcurrent protection components.
c. Radio communication battery: Radio communication uses more current than cell phone batteries and less current than laptop computers. The LR4 series has a working current of 7.3 amps, is small in size and light in weight, and is very suitable for this application. SRP or LTP series with large operating current is also applicable.
1.Application of resettable fuse in rechargeable battery pack
1) Problems and analysis: NICD, NiMH, Li-ION are often used in special protection circuits for mobile phones and computers.
The causes of these battery pack failures are usually: The positive and negative terminals are accidentally shorted; the charger cannot stop charging a fully charged battery; Reverse the polarity of the charger or battery. The PTC chip series is installed in series in each unit of the battery pack to provide overcurrent and overtemperature protection to the circuit.
2) Protection requirements: When a fault occurs, the voltage of the mobile phone can reach 16V, and the voltage of the computer can reach 24V; Its current can reach 100 amps. Under overcharge conditions, the battery pack needs to be protected from over-temperature. NiCD batteries cannot exceed 120C, and NiMH and Li-ION batteries cannot exceed 90C.
3) Selection of PTC components: LTP, VTP and LR4 are commonly used in mobile phones and cordless phones. SRP, LTP and LR4 series with higher holding current are often used in desktop and laptop computers. For NiMH battery packs, VTP and LTP materials allow designers to increase thermal conductivity protection. Some special application patches and VTP series can be used in AAA battery cells.
Applications: All high-density circuit boards
Features: Surface mount components, faster than ordinary SMD fuse action
Working current: 0.1A ~ 1.0A
Operating temperature range: -40 ℃ to 85 ℃
Lead-free, halogen-free environmentally friendly products, RoHS and REACH standards

Model
| Vmax | Imax | Ih | It | Pd | Time to trip | Resistance | |||
| V | A | A | A | W | Current(A) | Time(s) | Rmin(Ω) | R1max(Ω) | |
| SMD0603P005TF | 15.0 | 40 | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.00 | 2.000 | 10.000 |
| SMD0603P010TF | 15.0 | 40 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.00 | 0.900 | 6.000 |
| SMD0603P020TF | 9.0 | 40 | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.60 | 0.550 | 3.500 |
| SMD0603P025TF | 9.0 | 40 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.5 | 8.0 | 0.08 | 0.500 | 3.000 |
| SMD0603P035TF | 6.0 | 40 | 0.35 | 0.70 | 0.5 | 8.0 | 0.10 | 0.200 | 1.400 |
| SMD0603P050TF | 6.0 | 40 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.5 | 8.0 | 0.10 | 0.100 | 0.800 |
| SMD0603P075TF | 6.0 | 40 | 0.75 | 1.50 | 0.5 | 8.0 | 0.10 | 0.060 | 0.450 |
| SMD0603P100TF | 6.0 | 40 | 1.00 | 2.00 | 0.5 | 8.0 | 0.10 | 0.040 | 0.300 |
| SMD0603P110TF | 6.0 | 40 | 1.10 | 2.20 | 0.5 | 8.0 | 0.10 | 0.040 | 0.280 |
| Sign | Definition |
| Ih | Hold current-maximum current at which the device will not trip at 25℃ |
| It | Trip current-minimum current at which the device will always trip at 25℃ |
| Vmax | Maximum voltage at which the device will not trip |
| Vmaxi | Maximum voltage device can withstand without damage at it rated current |
| Imax | Maximum fault current device can withstand without damage at rated voltage |
| Rmin | Minimum device resistance at 25℃ prior to tripping |
| Rmax | Maximum device resistance at 25℃ prior to tripping |
| Figure | The Figure of PTC |
| Lead | Lead diameter |
PREV:PPTC Resettable Fuses model 0805
NEXT:NONE
NEXT:NONE











